Wednesday, 16 May 2007
3rd Floor Hall (Pfahler Hall)
187
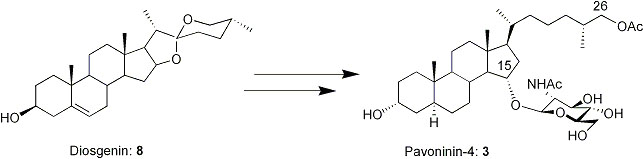
First Synthesis of the Shark Repellent Pavoninin-4
Steroidal saponins constitute a structurally and biologically diverse class of glycoconjugates which have been isolated from a wide variety of both plant and animal species. They are natural surfactants, and detergents. Fish belonging to the species Pardachirus pavoninus excrete a mixture of six steroidal N-acetylglucosaminides, pavoninins 1-6, with shark repelling properties. It is believed that the pavoninins are potent cell disrupters, which should have important pharmacological properties. We report the first synthesis of the shark repellent pavoninin-4, 3 by both direct synthesis from diosgenin and by remote functionalization. A good solution for glycosylation of hindered alcohols using glycosyl fluorides as good glycosyl donors and a highly efficient method for the chemoselective acetylation of the C-26 primary alcohol of the cholesterol skeleton in the presence of N-acetylglucosamine are also reported.
Back to Poster Session II
Back to The Middle Atlantic Regional Meeting (May 16 - 18, 2007)