Monday, May 19, 2008
Student Union Building, Upper (Queensborough Community College)
323
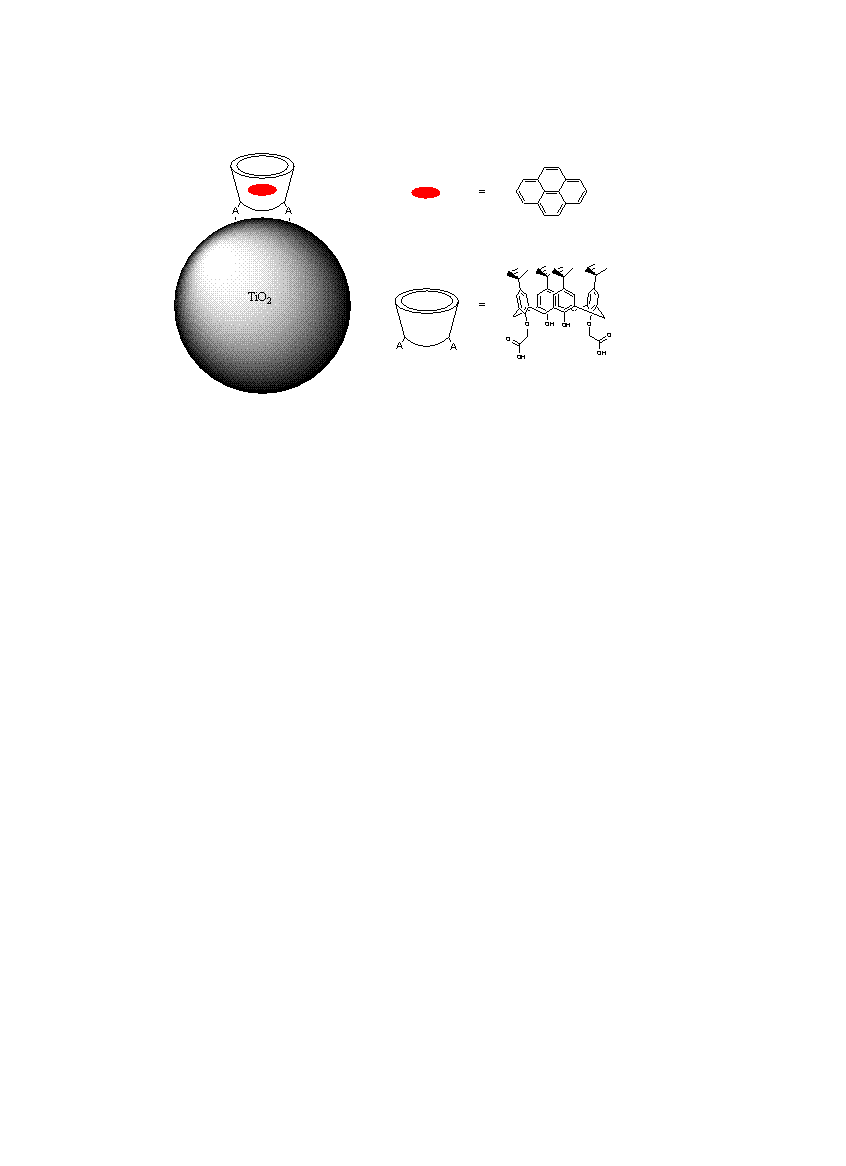
Organic Chromophores in Tert-Butylcalix[4]Arene for Metal Oxide Semiconductor Sensitization
Tert-butylcalix[4]arenes were used to encapsulate organic chromophores to form Dye@Host systems bound to colloidal TiO2 thin films via carboxylic acid anchor groups in different pH environments. The calix[4]arenes hosts are designed to insulate organic chromophores from each other to prevent aggregation effects, which could lower the efficiency of organic dye/semiconductor solar cells. The FT-IR-ATR spectra of Dye@Host systems bound to the TiO2 films showed the binding mode of the -COOH anchor groups in different pH environments. The UV-vis absorption and fluorescence emission of Dye@Host systems in solution and bound were compared at room temperature.