Monday, May 19, 2008 - 11:30 AM
Science Building, Rm S-111 (Queensborough Community College)
203
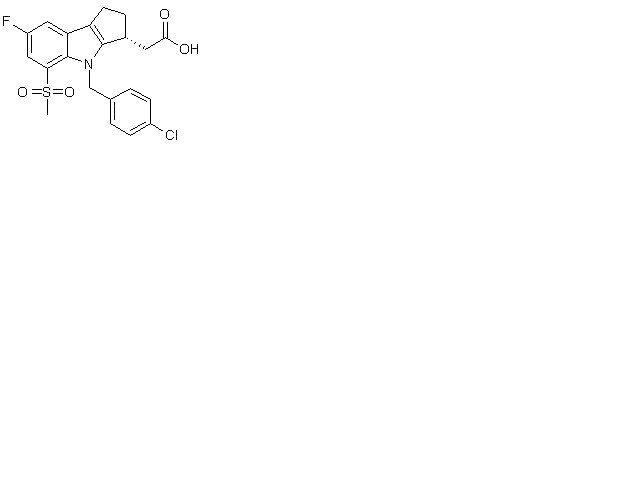
An Efficient Asymmetric Synthesis of the Tricyclic Indole Prostaglandin D2 Receptor Antagonist Laropiprant
An asymmetric synthesis was developed for the production of a prostaglandin D2 receptor antagonist for the treatment of allergic rhinitis. The stereogenic center was set using asymmetric hydrogenation, and the core of the structure was constructed via Fischer Indole methodology using a benzyl aryl hydrazine derived from a regioselective hydrazine alkylation. Several other synthetic approaches to the tricyclic indole system are also presented.