Wednesday, 16 May 2007 - 4:40 PM
208 (Pfahler Hall)
130
Tautomeric Modification of GlcNAc-Thiazoline
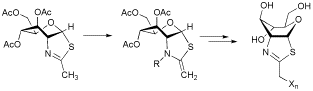
The potent O-GlcNAcase (OGA) inhibitor GlcNAc-thiazoline has been modified by buffer- or acylation-induced imine-to-enamine conversion, and then electrophile or radical addition (Xn = D3, F, N3, OH, SMe, COCF3, CF3). Several functionalized GlcNAc-thiazolines show highly selective inhibition of OGA vs human hexosaminidase, and thus have promise as tools for targeted investigations of OGA, an enzyme linked to diabetes and neurodegeneration. A new radical addition/fragmentation reaction of the N-(trifluoroacetyl)enamine has been discovered.
Back to Carbohydrate Chemistry/Glycoprotein
Back to The Middle Atlantic Regional Meeting (May 16 - 18, 2007)